For developersHow to Perform Vector Similarity Search Using Redis in NodeJS

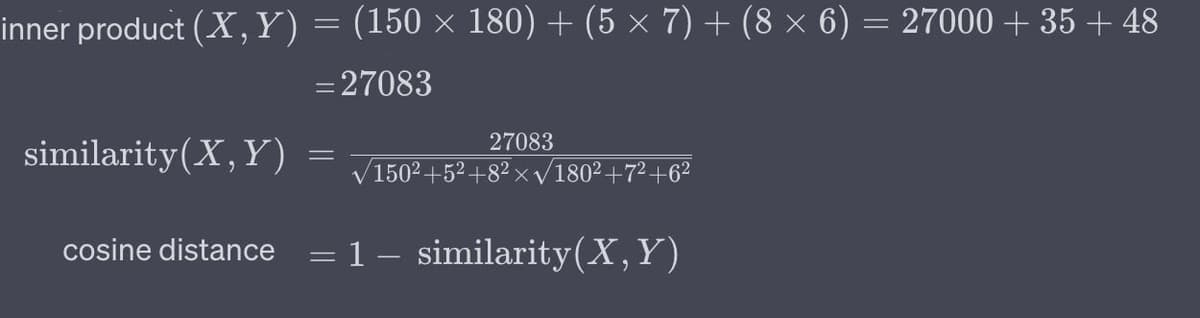
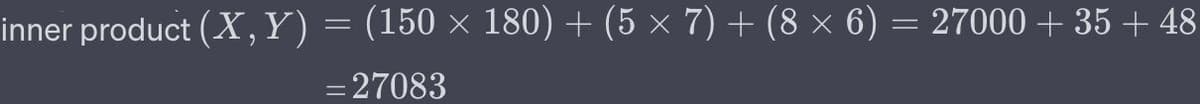
#What you will learn in this tutorial
This tutorial is a comprehensive guide to leveraging Redis for vector similarity search in a NodeJS environment. Aimed at software developers with expertise in the NodeJS/ JavaScript ecosystem, this tutorial will provide you with the knowledge and techniques required for advanced vector operations. Here's what's covered:
- About Vectors: Delve into the foundational concept of vectors in machine learning.
- Vector Databases: Understand specialized databases designed to handle vector data efficiently.
- Vector Similarity: Grasp the concept and significance of comparing vectors. Discover some use cases where vector similarity plays a pivotal role, from recommendation systems to content retrieval.
- Textual Content: Learn techniques to generate vectors from textual data.
- Imagery Content: Understand how images can be represented as vectors and how they're processed.
- Data Seeding: Get hands-on with populating your Redis database with vector data.
- Index Creation: Understand the process of indexing vector fields in Redis, optimizing for both accuracy and performance.
Advanced Vector Queries in Redis:
- KNN (k-Nearest Neighbors) Queries: Dive into the concept of KNN and its implementation in Redis to retrieve vectors most similar to a query vector.
- Range Queries: Discover how to retrieve vectors within a certain distance or range from a target vector.
Vector Similarity Calculations: (Optionally) if you want to understand the math behind vector similarity search
- Euclidean Distance: Understand the L2 norm method for calculating similarity.
- Cosine Similarity: Dive into the angular differences and its importance in vector space.
- Inner Product: Learn about another essential metric in understanding vector similarities.
Additional Resources: Take your learning further with other resources related to vectors in Redis.
#Vectors introduction
#What is a vector in machine learning?
In the context of machine learning, a vector is a mathematical representation of data. It is an ordered list of numbers that encode the features or attributes of a piece of data.
Vectors can be thought of as points in a multi-dimensional space where each dimension corresponds to a feature. For example, consider a simple dataset about ecommerce
products. Each product might have features such as price, quality, and popularity.| Id | Product | Price ($) | Quality (1 - 10) | Popularity (1 - 10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Puma Men Race Black Watch | 150 | 5 | 8 |
| 2 | Puma Men Top Fluctuation Red Black Watch | 180 | 7 | 6 |
| 3 | Inkfruit Women Behind Cream Tshirt | 5 | 9 | 7 |
Now, product 1
Puma Men Race Black Watch might be represented as the vector [150, 5, 8]In a more complex scenario, like natural language processing (NLP), words or entire sentences can be converted into dense vectors (often referred to as embeddings) that capture the semantic meaning of the text.Vectors play a foundational role in many machine learning algorithms, particularly those that involve distance measurements, such as clustering and classification algorithms.
#What is a vector database?
A vector database is a specialized system optimized for storing and searching vectors. Designed explicitly for efficiency, these databases play a crucial role in powering vector search apps, including recommendation systems, image search, and textual content retrieval. Often referred to as vector stores, vector indexes, or vector search engines, these databases employ vector similarity algorithms to identify vectors that closely match a given query vector.
TIPRedis Cloud is a popular choice for vector databases, as it offers a rich set of data structures and commands that are well-suited for vector storage and search. Redis Cloud allows you to index vectors and perform vector similarity search in a few different ways outlined further in this tutorial. It also maintains a high level of performance and scalability.
#What is vector similarity?
Vector similarity is a measure that quantifies how alike two vectors are, typically by evaluating the
distance or angle between them in a multi-dimensional space. When vectors represent data points, such as texts or images, the similarity score can indicate how similar the underlying data points are in terms of their features or content.#Use cases for vector similarity
- Recommendation Systems: If you have vectors representing user preferences or item profiles, you can quickly find items that are most similar to a user's preference vector.
- Image Search: Store vectors representing image features, and then retrieve images most similar to a given image's vector.
- Textual Content Retrieval: Store vectors representing textual content (e.g., articles, product descriptions) and find the most relevant texts for a given query vector.
CALCULATING VECTOR SIMILARITYIf you're interested in learning more about the mathematics behind vector similarity, scroll down to the How to calculate vector similarity? section.
#Generating vectors
In our scenario, our focus revolves around generating sentence (product description) and image (product image) embeddings or vectors. There's an abundance of AI model repositories, like GitHub, where AI models are pre-trained, maintained, and shared.
For sentence embeddings, we'll employ a model from Hugging Face Model Hub, and for image embeddings, one from TensorFlow Hub will be leveraged for variety.
GITHUB CODEBelow is a command to the clone the source code used in this tutorial
#Sentence/ text vector
To generate sentence embeddings, we'll make use of a Hugging Face model titled Xenova/all-distilroberta-v1. It's a compatible version of sentence-transformers/all-distilroberta-v1 for transformer.js with ONNX weights.
INFOHugging Face Transformers is a renowned open-source tool for Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. It simplifies the use of cutting-edge NLP models.The transformers.j library is essentially the JavaScript version of Hugging Face's popular Python library.
INFOONNX (Open Neural Network eXchange) is an open standard that defines a common set of operators and a common file format to represent deep learning models in a wide variety of frameworks, including PyTorch and TensorFlow
Below, you'll find a Node.js code snippet that illustrates how to create vector embeddings for any provided
sentence:Here's a glimpse of the vector output for a sample text:
#Image vector
To obtain image embeddings, we'll leverage the mobilenet model from TensorFlow.
Below, you'll find a Node.js code snippet that illustrates how to create vector embeddings for any provided image:

Below is an illustration of the vector output for a sample watch image:
#Database setup
GITHUB CODEBelow is a command to the clone the source code used in this tutorial
#Sample Data seeding
For the purposes of this tutorial, let's consider a simplified e-commerce context. The
products JSON provided offers a glimpse into vector search functionalities we'll be discussing.Below is the sample code to seed products data as JSON in Redis. The data also includes vectors of both product descriptions and images.
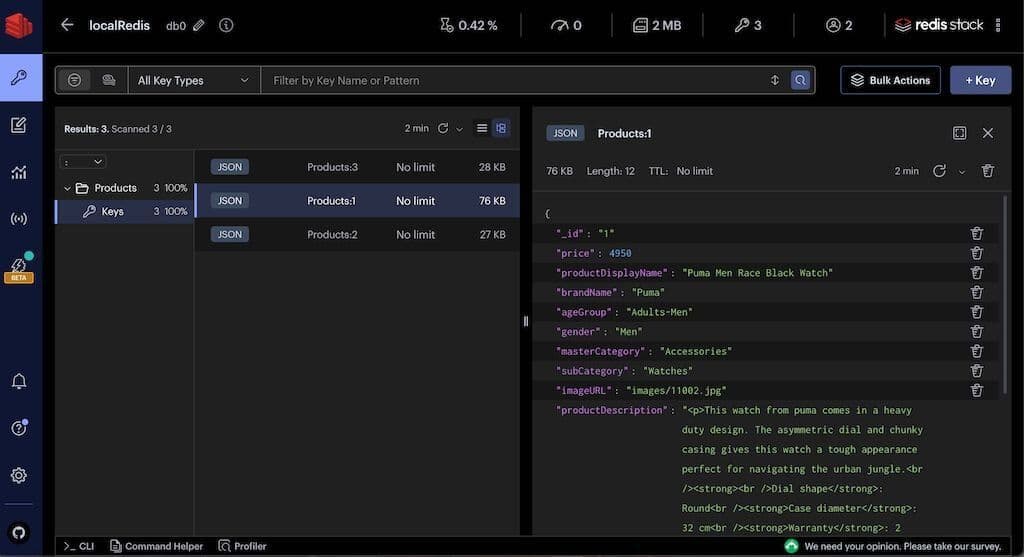
You can observe products JSON data in Redis Insight:

TIPDownload Redis Insight to visually explore your Redis data or to engage with raw Redis commands in the workbench.
#Create vector index
For searches to be conducted on JSON fields in Redis, they must be indexed. The methodology below highlights the process of indexing different types of fields. This encompasses vector fields such as
productDescriptionEmbeddings and productImageEmbeddings.FLAT VS HNSW INDEXINGFLAT: When vectors are indexed in a "FLAT" structure, they're stored in their original form without any added hierarchy. A search against a FLAT index will require the algorithm to scan each vector linearly to find the most similar matches. While this is accurate, it's computationally intensive and slower, making it ideal for smaller datasets.HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World): HNSW is a graph-centric method tailored for indexing high-dimensional data. With larger datasets, linear comparisons against every vector in the index become time-consuming. HNSW employs a probabilistic approach, ensuring faster search results but with a slight trade-off in accuracy.
INITIAL_CAP AND BLOCK_SIZE PARAMETERSBoth INITIAL_CAP and BLOCK_SIZE are configuration parameters that control how vectors are stored and indexed.INITIAL_CAP defines the initial capacity of the vector index. It helps in pre-allocating space for the index.BLOCK_SIZE defines the size of each block of the vector index. As more vectors are added, Redis will allocate memory in chunks, with each chunk being the size of the BLOCK_SIZE. It helps in optimizing the memory allocations during index growth.
#What is vector KNN query?
KNN, or k-Nearest Neighbors, is an algorithm used in both classification and regression tasks, but when referring to "KNN Search," we're typically discussing the task of finding the "k" points in a dataset that are closest (most similar) to a given query point. In the context of vector search, this means identifying the "k" vectors in our database that are most similar to a given query vector, usually based on some distance metric like cosine similarity or Euclidean distance.
#Vector KNN query with Redis
Redis allows you to index and then search for vectors using the KNN approach.
Below, you'll find a Node.js code snippet that illustrates how to perform
KNN query for any provided search text:Please find output for a KNN query in Redis (A lower score or distance in the output signifies a higher degree of similarity.)
NOTEKNN queries can be combined with standard Redis search functionalities using Hybrid queries.
#What is vector range query?
Range queries retrieve data that falls within a specified range of values. For vectors, a "range query" typically refers to retrieving all vectors within a certain distance of a target vector. The "range" in this context is a radius in the vector space.
#Vector range query with Redis
Below, you'll find a Node.js code snippet that illustrates how to perform vector
range query for any range (radius/ distance)provided:Please find output for a range query in Redis
#Image vs text vector query
IMAGE VS TEXT VECTOR QUERYThe syntax for vector KNN/ range queries is consistent, regardless of whether you're working with image vectors or text vectors. Just as there's a method for text vector queries namedqueryProductDescriptionEmbeddingsByKNN, there's a corresponding method for images titledqueryProductImageEmbeddingsByKNNin the code base.
GITHUB CODEBelow is a command to clone the source code used in this tutorial
Hopefully this tutorial has helped you visualize how to use Redis for vector similarity search.
(Optional) If you want to also understand the math behind vector similarity search , then read following
#How to calculate vector similarity?
Several techniques are available to assess vector similarity, with some of the most prevalent ones being:
#Euclidean Distance (L2 norm)
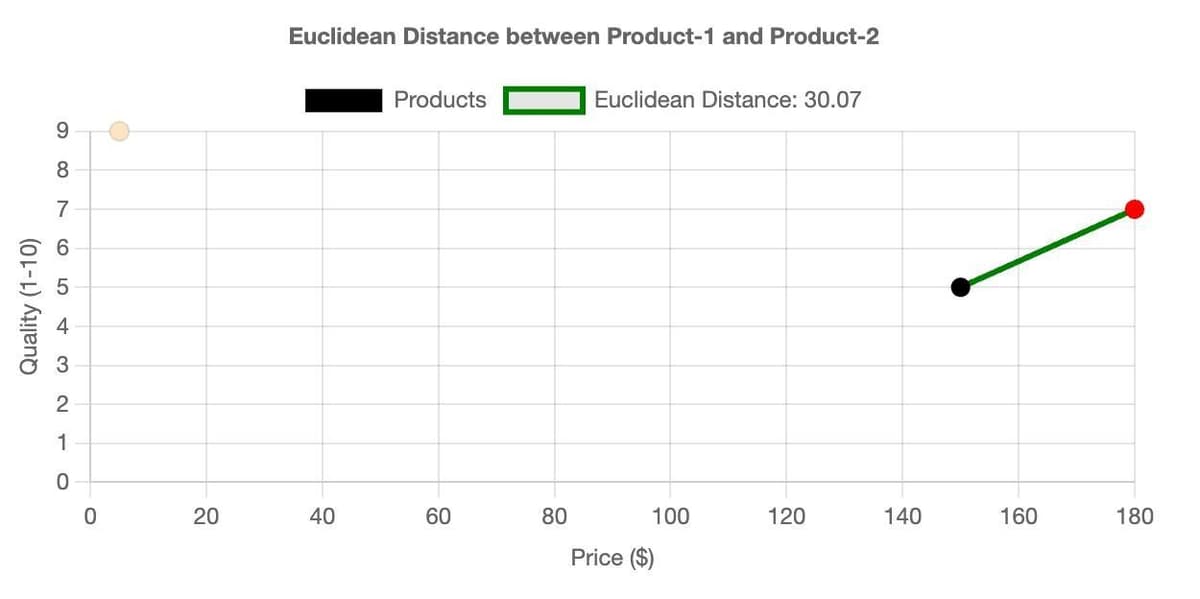
Euclidean Distance (L2 norm) calculates the linear distance between two points within a multi-dimensional space. Lower values indicate closer proximity, and hence higher similarity.
For illustration purposes, let's assess
product 1 and product 2 from the earlier ecommerce dataset and determine the Euclidean Distance considering all features.As an example, we will use a 2D chart made with chart.js comparing the
Price vs. Quality features of our products, focusing solely on these two attributes to compute the Euclidean Distance.
#Cosine Similarity
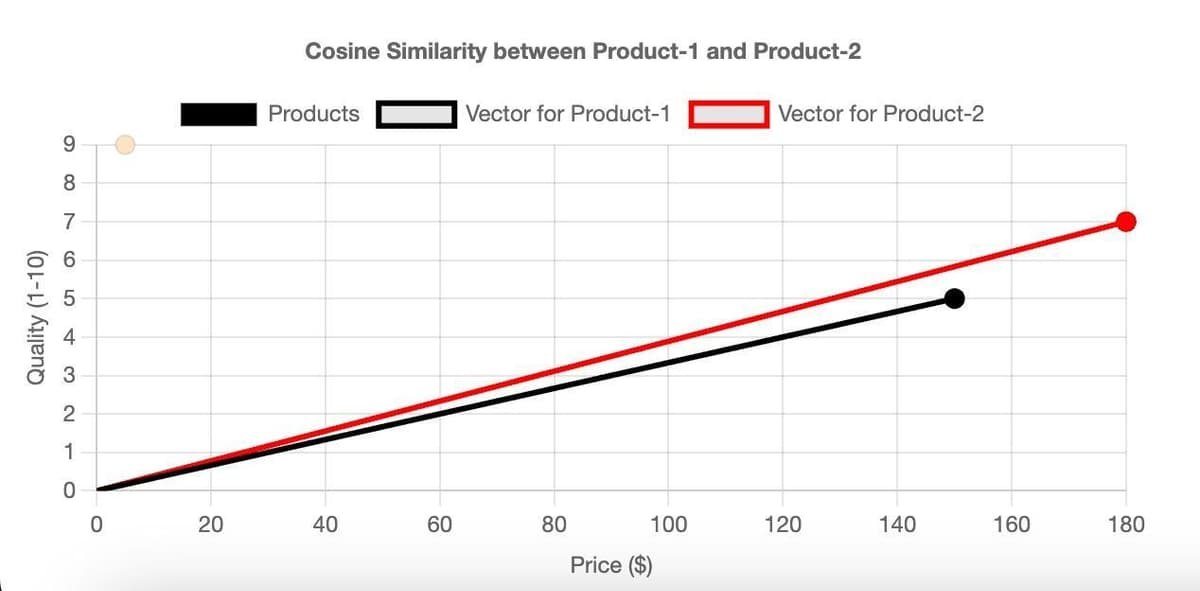
Cosine Similarity measures the cosine of the angle between two vectors. The cosine similarity value ranges between -1 and 1. A value closer to 1 implies a smaller angle and higher similarity, while a value closer to -1 implies a larger angle and lower similarity. Cosine similarity is particularly popular in NLP when dealing with text vectors.
NOTEIf two vectors are pointing in the same direction, the cosine of the angle between them is 1. If they're orthogonal, the cosine is 0, and if they're pointing in opposite directions, the cosine is -1.
Again, consider
product 1 and product 2 from the previous dataset and calculate the Cosine Distance for all features.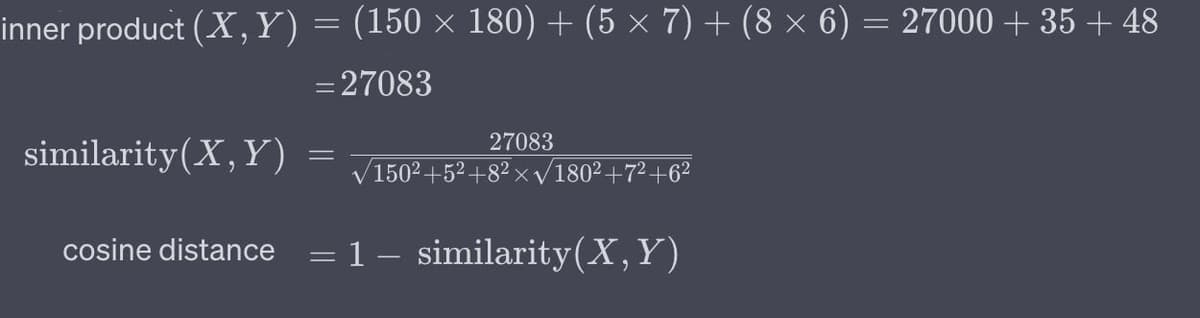
Using chart.js, we've crafted a 2D chart of
Price vs. Quality features. It visualizes the Cosine Similarity solely based on these attributes.
#Inner Product
Inner Product (dot product) The inner product (or dot product) isn't a distance metric in the traditional sense but can be used to calculate similarity, especially when vectors are normalized (have a magnitude of 1). It's the sum of the products of the corresponding entries of the two sequences of numbers.
NOTEThe inner product can be thought of as a measure of how much two vectors "align" in a given vector space. Higher values indicate higher similarity. However, the raw values can be large for long vectors; hence, normalization is recommended for better interpretation. If the vectors are normalized, their dot product will be1 if they are identicaland0 if they are orthogonal(uncorrelated).
Considering our
product 1 and product 2, let's compute the Inner Product across all features.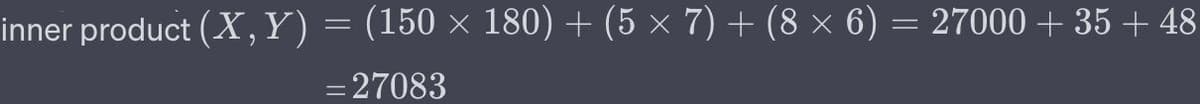
TIPVectors can also be stored in databases in binary formats to save space. In practical applications, it's crucial to strike a balance between the dimensionality of the vectors (which impacts storage and computational costs) and the quality or granularity of the information they capture.

